RBAC and Namespace Support
RoleBindings and ClusterRoleBindings are Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) concepts that allow granular control over cluster-wide resources. Palette provides you the ability to specify bindings to configure granular RBAC rules.
You can configure namespaces and RBAC from within a cluster or from a Palette Workspace that contains a collection of like clusters that need to be managed as a group. If a host cluster is part of a Palette workspace, then all roleBindings must occur at the namespace level.
As you review RBAC support, use the following definitions:
-
Role An entity that is assigned a set of access permissions within a namespace. Roles require the assignment of a Kubernetes namespace.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: default
name: pod-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"] -
Cluster Role An entity that is assigned a set of access permissions scoped to the cluster and all of its Kubernetes namespaces. ClusterRoles do not have a namespace assigned.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: secret-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["secrets"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"] -
RoleBinding associates a subject with a role. A subject can be a user, a group, or a ServiceAccount. Role binding is used to grant permissions to a subject. Role and RoleBinding are used to scope a subject to a specific Kubernetes namespace.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: read-pods
namespace: default
subjects:
- kind: User
name: jane
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: pod-reader
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io -
ClusterRoleBinding associates a subject with a ClusterRole. A subject can be a user, a group, or a ServiceAccount. A ClusterRoleBinding is used to grant permissions to a subject. ClusterRole and ClusterRoleBinding are used to scope a subject's access to the cluster which includes all the Kubernetes namespaces inside the cluster.
There are many reasons why you may want to create roles and assign permissions to different users or groups. Below are a few common scenarios.
- Use Role and a RoleBinding to scope security to a single Kubernetes namespace.
- Use Role and a RoleBinding to scope security to several Kubernetes namespaces.
- Use ClusterRole and ClusterRoleBinding to scope security to all namespaces.
Palette does not provide a way for roles to be configured natively through its platform. You can create roles by using a manifest layer in the cluster profile. RBAC management only allows you to specify role bindings.
Use the steps below to create a RoleBinding or ClusterRoleBinding for your host clusters.
Palette Roles and Kubernetes Roles
Palette offers a set of default roles you can assign to your users. The Palette roles are only in scope at the platform level. This means you can manage the permissions for users' actions in Palette, such as creating or deleting clusters, creating projects, creating users, and more.
The Kubernetes roles are used to control the actions users are allowed to do inside the cluster. For example, a user in Palette could have the Cluster Profile Viewer role, which grants them the ability to view cluster profiles for a specific project. In all the clusters in this project, the user could be assigned a role binding to a custom role that grants them administrative access in all the clusters.
In summary, using Palette roles allows you to control what actions users can do in Palette. Use Kubernetes roles to control users' actions inside a host cluster.
Palette roles do not automatically map to a Kubernetes role. You must create a role binding for a specific user or group of users.
Create Role Bindings
Prerequisites
To create a role binding the role must exist inside the host cluster. You can use any of the default cluster roles provided by Kubernetes. The alternative to default cluster roles is to create a role by using a manifest in the cluster profile.
If you have OpenID Connect (OIDC) configured at the Kubernetes layer of your cluster profile, you can create a role binding that maps individual users or groups assigned within the OIDC provider's configuration to a role. To learn more, review Use RBAC with OIDC.
Enablement
You can create role bindings during the cluster creation process or after the host cluster is deployed.
For a new cluster, you can modify the cluster settings at the end of the cluster creation process. RBAC is one of the cluster settings you can modify. Select RBAC from the left Settings Menu.
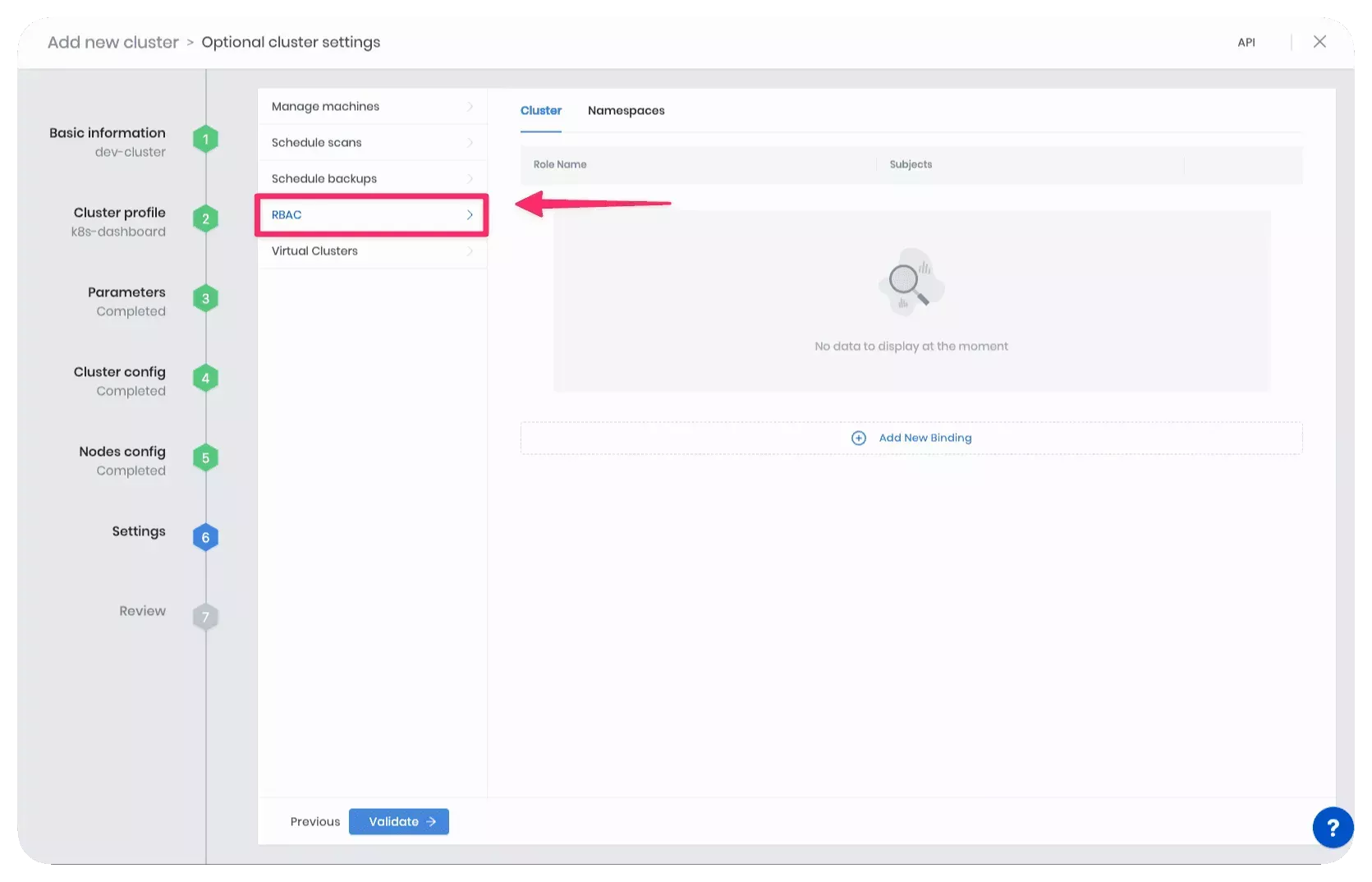
To create or modify a role binding for an active cluster. Navigate to the cluster details page and click on Settings. Select RBAC from the left Settings Menu.
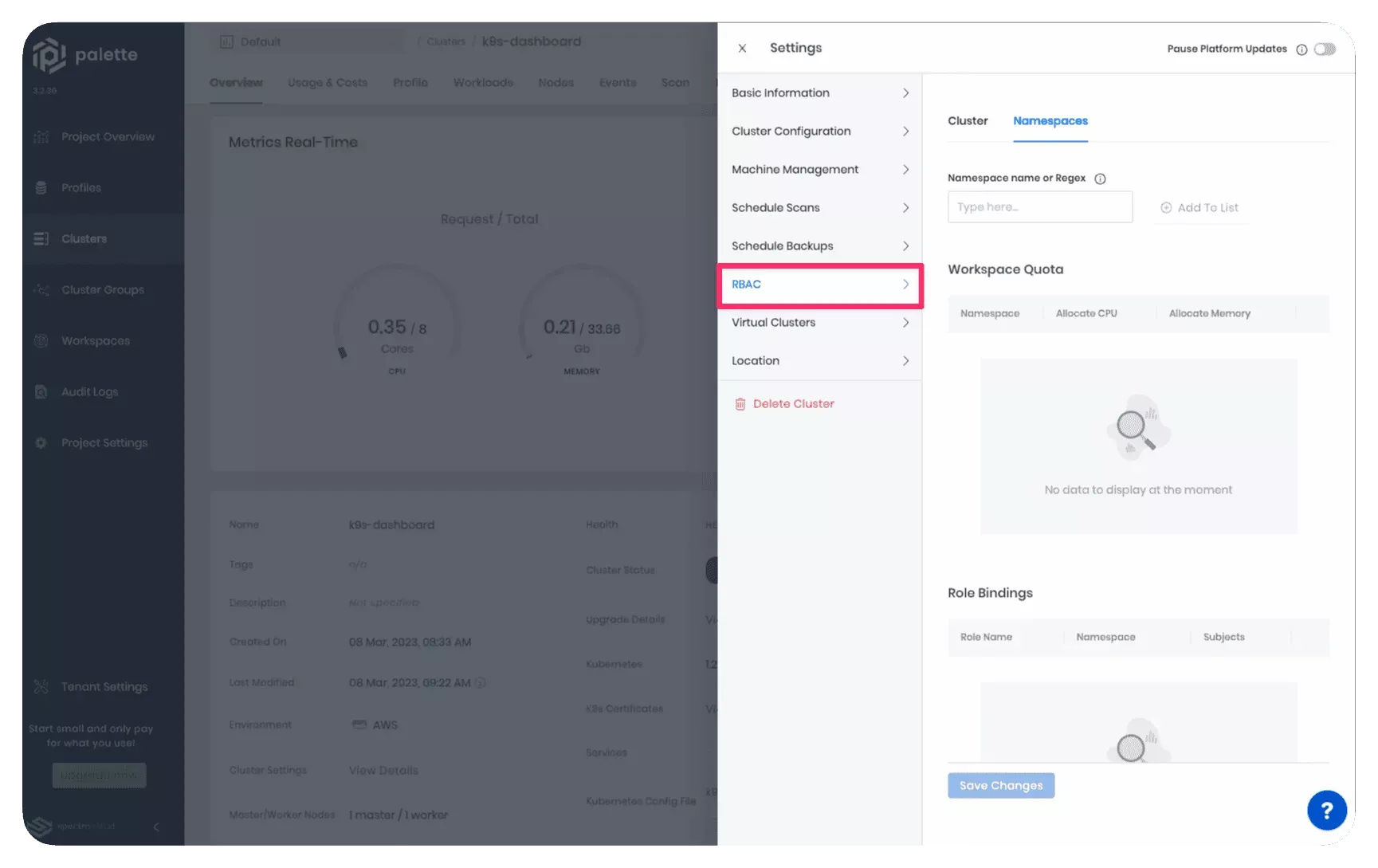
The RBAC settings view contains two tabs:
- Cluster: Use this tab to create a ClusterRoleBinding.
- Namespaces: Use this tab to create a RoleBinding within Kubernetes namespaces.
Select the tab for your specific role scope to learn how to create the appropriate role binding.
- Assign a Cluster Role
- Assign a Namespace Role
-
From the cluster settings view, select the RBAC tab.
-
Click on Add New Binding.
-
Fill out the following details:
- Role Name: Define a custom role name to identify the cluster role.
- Subjects: Subjects are a group of users, services, or teams using the Kubernetes API. If you are using Palette as your IDP, you can use the Palette user's registration email address to identify the user.
- Subject Name: Custom name to identify a subject.
In Kubernetes, a role binding connects a user or group with a set of permissions called a Role. The Role can be in the same namespace as the RoleBinding. If you want to give a role access to all the namespaces in your cluster, use a ClusterRoleBinding.
- Click on Confirm to save your changes.
A ClusterRoleBinding will be created in your host cluster. Keep in mind that you can assign multiple subjects to a ClusterRoleBinding.
-
From the cluster settings view, select the RBAC tab.
-
Click on Add New Binding.
-
Add the namespace name or provide a regular expression to automatically apply the following settings to other namespaces in the future. Example:
/^web-app/. Click on Add To List. -
Allocate resources to the selected namespace. You can allocate the maximum CPU and Memory the role is allowed to consume from the listed namespaces.
-
Click on Add New Binding.
-
Fill out the following details:
- Namespace: Select the namespace.
- Role Type: The type of role. You can specify either a role or a cluster role.
- Role Name: Define a custom role name to identify the cluster role.
- Subjects: Subjects are a group of users, services, or teams using the Kubernetes API.
- Subject Name: Custom name to identify a subject.
In Kubernetes, a role binding connects a user or group with a set of permissions called a Role. The Role can be in the same namespace as the RoleBinding. If you want to give a role access to all the namespaces in your cluster, use a ClusterRoleBinding.
A role binding will be created in the listed namespaces. Keep in mind that you can assign multiple subjects to a RoleBinding or ClusterRoleBinding.
Validate
-
Log in to Palette.
-
Navigate to the left Main Menu and select Clusters.
-
Select the cluster you created the role binding in to view its details page.
-
Download the kubeconfig file for the cluster or use the web shell to access the host cluster.
-
Use the following commands to review details about the role and to ensure the role binding was successful.
Cluster Role:
kubectl get clusterrole <yourRoleNameHere> --output yaml
Role
kubectl get role <yourRoleNameHere> --namespace <namespace> --show-kind --export