Create Migration Plans
Follow this guide to create migration plans using the VM Migration Assistant.
Limitations
-
You can migrate only VMs hosted in VMware vSphere 7.0 or 8.0.
-
You can migrate only VMs whose operating systems are present in the
virt-v2vsupported guest systems list. Refer to Verified Migrations for a list of operating systems and migration combinations verified by Spectro Cloud. -
If you are migrating more than one VM in the same plan, they must all share the same network.
Prerequisites
-
At least one source provider for the VMs to be migrated. Refer to Create Source Providers for guidance.
-
A healthy Virtual Machine Orchestrator (VMO) cluster. Refer to the Create a VMO Profile for further guidance.
- The VMO cluster must have network connectivity to vCenter and ESXi hosts, and the VMs you want to migrate.
warningIf you need to provision
Blockstorage volumes during the VM migration process, add the following custom configuration to your VMO cluster OS pack. Applying this configuration may cause a cluster repave. For more information, refer to Repave Behaviors and ConfigurationsAdditionally, we recommend provisioning volumes with the
ReadWriteManyaccess mode to ensure that VMs can be live migrated.kubeadmconfig:
preKubeadmCommands:
# Start containerd with new configuration
- systemctl daemon-reload
- systemctl restart containerd
files:
- targetPath: /etc/containerd/config.toml
targetOwner: "root:root"
targetPermissions: "0644"
content: |
## template: jinja
# Use config version 2 to enable new configuration fields.
version = 2
imports = ["/etc/containerd/conf.d/*.toml"]
[plugins]
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri"]
sandbox_image = "registry.k8s.io/pause:3.9"
device_ownership_from_security_context = true
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.runtimes.runc]
runtime_type = "io.containerd.runc.v2"
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.runtimes.runc.options]
SystemdCgroup = true -
One or more VMs hosted in VMware vSphere.
- For cold migrations, ensure that VMs operating Windows are shut down at the guest OS level.
- For warm migrations, Changed Block Tracking must be enabled on your VMs.
-
The Virtual Machine Migration Assistant pack must be added to your cluster profile. Refer to Create a VM Migration Assistant Cluster Profile for guidance.
- The VM Migration Assistant service console must be accessible from a web browser.
-
We recommend using a ConfigMap to uninstall VMware Tools, and install the QEMU Guest Agent and VirtiIO drivers on your migrated VMs. Installing the QEMU agent and Virtio drivers enhances compatibility with VMO, and enables advanced features like live migration and accurate reporting of guest status.
You can provide virt-customize scripts inside a ConfigMap to automatically perform these actions on your VMs during migration. The ConfigMap must exist in your target namespace before migrating your VMs.
Example steps to create a ConfigMap that deploys virt-customize scripts
-
Use the following example to create a YAML file named
configmap.yaml.apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: forklift-virt-customize
namespace: my-vm-migration-namespace
data:
00_linux_firstboot_install_vmtools.sh: |
#!/bin/bash
set -eo pipefail
# Global variables
LOGFILE="/var/log/vm_tools_management.log"
DRYRUN=false
# Logging function
log() {
echo "[$(date +'%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')] $*" | tee -a "$LOGFILE"
}
# Function to detect the Linux distribution
detect_distro() {
if [ -f /etc/os-release ]; then
. /etc/os-release
echo "$ID"
elif [ -f /etc/lsb-release ]; then
. /etc/lsb-release
echo "$DISTRIB_ID" | tr '[:upper:]' '[:lower:]'
elif [ -f /etc/redhat-release ]; then
echo "rhel"
else
echo "unknown"
fi
}
# Function to detect the system architecture
detect_arch() {
uname -m
}
# Function to set package manager variables
set_package_manager() {
case "$distro" in
ubuntu|debian)
PKG_MANAGER="apt-get"
PKG_UPDATE="$PKG_MANAGER update"
PKG_INSTALL="$PKG_MANAGER install -y"
PKG_REMOVE="$PKG_MANAGER remove -y"
PKG_QUERY="dpkg -l"
;;
rhel|centos|fedora)
if command -v dnf >/dev/null; then
PKG_MANAGER="dnf"
else
PKG_MANAGER="yum"
fi
PKG_UPDATE="$PKG_MANAGER makecache"
PKG_INSTALL="$PKG_MANAGER install -y"
PKG_REMOVE="$PKG_MANAGER remove -y"
PKG_QUERY="rpm -q"
;;
opensuse|sles|opensuse-leap)
PKG_MANAGER="zypper"
PKG_UPDATE="$PKG_MANAGER refresh"
PKG_INSTALL="$PKG_MANAGER install -y"
PKG_REMOVE="$PKG_MANAGER remove -y"
PKG_QUERY="rpm -q"
;;
arch)
PKG_MANAGER="pacman"
PKG_UPDATE="$PKG_MANAGER -Sy"
PKG_INSTALL="$PKG_MANAGER -S --noconfirm"
PKG_REMOVE="$PKG_MANAGER -Rns --noconfirm"
PKG_QUERY="pacman -Q"
;;
*)
log "Error: Unsupported distribution"
exit 1
;;
esac
}
# Function to get distribution-specific package names
get_package_name() {
local generic_name="$1"
case "$distro" in
ubuntu|debian)
case "$generic_name" in
qemu-guest-agent) echo "qemu-guest-agent" ;;
virtio-tools) echo "virtio-win" ;;
open-vm-tools) echo "open-vm-tools" ;;
cloud-init) echo "cloud-init" ;;
*) echo "$generic_name" ;;
esac
;;
rhel|centos|fedora)
case "$generic_name" in
qemu-guest-agent) echo "qemu-guest-agent" ;;
virtio-tools) echo "virtio-win" ;;
open-vm-tools) echo "open-vm-tools" ;;
cloud-init) echo "cloud-init" ;;
*) echo "$generic_name" ;;
esac
;;
opensuse|sles)
case "$generic_name" in
qemu-guest-agent) echo "qemu-guest-agent" ;;
virtio-tools) echo "virtio-drivers" ;;
open-vm-tools) echo "open-vm-tools" ;;
cloud-init) echo "cloud-init" ;;
*) echo "$generic_name" ;;
esac
;;
arch)
case "$generic_name" in
qemu-guest-agent) echo "qemu-guest-agent" ;;
virtio-tools) echo "linux-virtio" ;;
open-vm-tools) echo "open-vm-tools" ;;
cloud-init) echo "cloud-init" ;;
*) echo "$generic_name" ;;
esac
;;
esac
}
# Function to update package manager repositories
update_repos() {
if [ "$DRYRUN" = true ]; then
log "Dry run: Would update package repositories"
return
fi
log "Updating package repositories..."
if $PKG_UPDATE; then
log "Package repositories updated successfully"
else
log "Error: Failed to update package repositories"
exit 1
fi
}
# Function to install packages
install_package() {
local package=$(get_package_name "$1")
if [ -z "$PKG_MANAGER" ]; then
log "Error: Package manager not set"
return 1
fi
if [ "$DRYRUN" = true ]; then
log "Dry run: Would install $package"
return
fi
log "Installing $package..."
if $PKG_INSTALL "$package"; then
log "$package installed successfully"
else
log "Error: Failed to install $package"
return 1
fi
}
# Function to check if a package is installed
is_installed() {
local package=$(get_package_name "$1")
$PKG_QUERY "$package" >/dev/null 2>&1
}
# Function to handle Virtio drivers
handle_virtio_drivers() {
if lsmod | grep -qE "virtio_net|virtio_blk|virtio_scsi"; then
log "Virtio drivers are already installed and active."
else
log "Virtio drivers are not loaded. Attempting to install..."
if ! install_package virtio-tools; then
log "No separate virtio-tools package available. Virtio may be built into the kernel."
if [ "$DRYRUN" = false ]; then
modprobe virtio_net virtio_blk virtio_scsi || log "Failed to load Virtio modules"
else
log "Dry run: Would attempt to load Virtio modules"
fi
fi
fi
}
# Function to handle QEMU guest agent
handle_qemu_agent() {
local package=$(get_package_name "qemu-guest-agent")
if is_installed "$package"; then
log "QEMU guest agent is already installed."
if [ "$DRYRUN" = false ]; then
if systemctl is-active --quiet qemu-guest-agent; then
log "QEMU guest agent service is running."
else
log "Starting QEMU guest agent service..."
systemctl start qemu-guest-agent || log "Failed to start QEMU guest agent service"
fi
else
log "Dry run: Would check and potentially start QEMU guest agent service"
fi
else
log "QEMU guest agent is not installed. Installing..."
if install_package "$package"; then
if [ "$DRYRUN" = false ]; then
log "Starting QEMU guest agent service..."
systemctl start qemu-guest-agent || log "Failed to start QEMU guest agent service"
else
log "Dry run: Would start QEMU guest agent service"
fi
fi
fi
}
# Function to handle VMware Tools daemon (vmtoolsd)
handle_vmtoolsd() {
local package=$(get_package_name "open-vm-tools")
if is_installed "$package"; then
log "VMware Tools daemon (vmtoolsd) is installed."
if [ "$DRYRUN" = false ]; then
if pgrep -f vmware-vmx > /dev/null; then
log "Warning: VMware virtual machines are running. Skipping uninstallation."
return
fi
log "Uninstalling VMware Tools daemon..."
if $PKG_REMOVE "$package"; then
log "VMware Tools daemon uninstalled successfully."
else
log "Error: Failed to uninstall VMware Tools daemon."
fi
else
log "Dry run: Would uninstall VMware Tools daemon"
fi
else
log "VMware Tools daemon (vmtoolsd) is not installed."
fi
}
# Function to handle Cloud-init
handle_cloud_init() {
local package=$(get_package_name "cloud-init")
if is_installed "$package"; then
log "Cloud-init is already installed."
if [ "$DRYRUN" = false ]; then
if systemctl is-active --quiet cloud-init; then
log "Cloud-init service is running."
else
log "Starting Cloud-init service..."
systemctl start cloud-init || log "Failed to start Cloud-init service"
fi
else
log "Dry run: Would check and potentially start Cloud-init service"
fi
else
log "Cloud-init is not installed. Installing..."
if install_package "$package"; then
if [ "$DRYRUN" = false ]; then
log "Starting Cloud-init service..."
systemctl start cloud-init || log "Failed to start Cloud-init service"
else
log "Dry run: Would start Cloud-init service"
fi
fi
fi
}
# Function to check if running in a virtual environment
check_virtual_env() {
if [ -d /proc/vz ]; then
log "OpenVZ environment detected"
return 0
elif [ -d /proc/xen ]; then
log "Xen environment detected"
return 0
elif [ "$(systemd-detect-virt)" != "none" ]; then
log "Virtual environment detected: $(systemd-detect-virt)"
return 0
else
log "No virtual environment detected"
return 1
fi
}
# Parse command line options
parse_options() {
while getopts ":hvqd" opt; do
case ${opt} in
h )
echo "Usage: $0 [-h] [-v] [-q] [-d]"
echo " -h Display this help message"
echo " -v Verbose mode"
echo " -q Quiet mode"
echo " -d Dry run"
exit 0
;;
v )
set -x
;;
q )
exec 1>/dev/null 2>&1
;;
d )
DRYRUN=true
;;
\? )
echo "Invalid Option: -$OPTARG" 1>&2
exit 1
;;
esac
done
shift $((OPTIND -1))
}
# Main script
main() {
parse_options "$@"
log "Detecting system information..."
distro=$(detect_distro)
arch=$(detect_arch)
log "Detected distribution: $distro"
log "Detected architecture: $arch"
if [ "$distro" = "unknown" ]; then
log "Unable to detect distribution. Please proceed manually."
exit 1
fi
set_package_manager
if ! check_virtual_env; then
log "Warning: This script is intended for virtual environments. Proceed with caution."
fi
log "Ensuring package manager repositories are up to date..."
update_repos
log "Handling Virtio drivers..."
handle_virtio_drivers
log "Handling QEMU guest agent..."
handle_qemu_agent
log "Handling VMware Tools daemon (vmtoolsd)..."
handle_vmtoolsd
log "Handling Cloud-init..."
handle_cloud_init
log "All tasks completed."
}
main "$@"
01_linux_run.sh: |
#!/bin/bash
echo "running a run script. nothing to do"
00_win_firstboot.ps1: |
param (
[string]$LogFile = "C:\vm_tools\installation-check.log",
[switch]$VerboseOutput = $false
)
# Function to log and write output
function Write-Log {
param (
[string]$Message
)
Write-Output $Message
Add-Content -Path $LogFile -Value $Message
}
# Create or clear log file
if (Test-Path $LogFile) {
Clear-Content -Path $LogFile
} else {
New-Item -Path $LogFile -ItemType File -Force
}
# Check for VirtIO Drivers
Write-Log "Checking for VirtIO Drivers..."
$VirtIODrivers = Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_PnPSignedDriver | Where-Object {
$_.DeviceName -like "*VirtIO*" -or $_.DriverProviderName -like "*Red Hat*"
}
if ($VirtIODrivers) {
Write-Log "VirtIO Drivers are installed."
} else {
Write-Log "VirtIO Drivers are NOT installed."
}
# Check for QEMU Agent
Write-Log "Checking for QEMU Guest Agent..."
$QemuAgentInstalled = Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_Product | Where-Object {
$_.Name -like "*QEMU*"
}
if ($QemuAgentInstalled) {
Write-Log "QEMU Guest Agent is installed."
} else {
Write-Log "QEMU Guest Agent is NOT installed."
}
# Check for VMware Tools (vmtoolsd)
Write-Log "Checking for VMware Tools (vmtoolsd)..."
$VmToolsInstalled = Get-Command -Name "vmtoolsd.exe" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
if ($VmToolsInstalled) {
Write-Log "VMware Tools (vmtoolsd) is installed."
} else {
Write-Log "VMware Tools (vmtoolsd) is NOT installed."
}
# Verbose Output
if ($VerboseOutput) {
Get-Content -Path $LogFile
}
Write-Log "Check completed. Log saved to $LogFile." -
Make any changes that you need, but ensure that
metadata.nameis set toforklift-virt-customize, andmetadata.namespaceis set to your target VM migration namespace.Format rules:
- Windows scripts must follow the regex
^([0-9]+_win_firstboot(([\w\-]*).ps1))$.- For example,
00_win_firstboot.ps1is a PowerShell script that executes at boot.
- For example,
- Linux scripts must follow the regex
^([0-9]+_linux_(run|firstboot)(([\w\-]*).sh))$.firstbootmeans execute at first boot.runmeans execute after virt-v2v conversion, but before the VM starts.
- The number at the beginning of the key determines the script execution order.
- Windows scripts must follow the regex
-
Ensure that your terminal is configured to access your VMO cluster and issue the following command to create the ConfigMap on your cluster.
kubectl apply --filename configmap.yaml
-
Create Migration Plan
-
From the left Main Menu, select Plans for virtualization.
-
In the top-left corner, use the Namespace drop-down Menu to select your Kubernetes namespace for the migration.
-
In the top-right corner, click Create Plan.
-
Click on your source provider to select it, the Select virtual machines table appears.
-
For each VM that you want to migrate, click the checkbox next to the VM name. You can use the filters at the top of the table to help you search.
-
Once you have selected your VMs, click Next.
-
Fill in the migration plan details.
Setting Description Example Plan name A unique name for your migration plan. myMigrationPlanTarget provider Select the target provider from the drop-down Menu. By default, this will be your VMO cluster. hostTarget namespace Select the target namespace from the drop-down Menu. The target namespace is where the migrated VMs will be located on your VMO cluster. myVmMigrationNamespaceNetwork map A network map defines the mapping of source networks to target networks, ensuring VM network interfaces are correctly connected in the destination environment. Adjust the mapping, or leave the default mapping in place. VM Network/Pod NetworkingStorage map A storage map defines the mapping of source storage domains to target storage classes or datastores, ensuring VM disks are correctly placed in the destination environment. Adjust the mapping, or leave the default mapping in place. vsanDatastore/spectro-storage-classPreserve static IPs Choose whether to preserve the static IPs of the VMs migrated from vSphere. ✅ -
Click Create migration plan. The Details tab for the plan is then displayed.
-
Review the Details tab and check that the following settings are configured to your requirements.
If you need to change a setting, click the pencil icon next to each value and adjust it in the pop-up window. Click Save after making changes.
Setting Description Warm migration Choose whether this will be a warm or cold migration. A cold migration is when VMs are shut down at the start of migration. A warm migration is when VMs are shut down during the final switchover. Target namespace The target namespace for the migrated VMs. Disk decryption passphrases Provide a list of passphrases for LUKS-encrypted devices on the VMs you intend to migrate. Transfer Network Change the migration transfer network for this plan. If a migration transfer network is defined for the source provider and exists in the target namespace, it is used by default. Otherwise, the pod network is used. Preserve static IPs Choose whether to preserve the static IPs of the VMs migrated from vSphere. Root device Choose the root filesystem to convert. By default, the first root device is chosen in multi-boot systems. You can specify a root device, for example, /dev/sda1, for multi-boot systems, but if it is not detected as a root device, the migration will fail.If you want to explore all additional plan settings, refer to the Additional Configuration - Plan Settings for guidance.
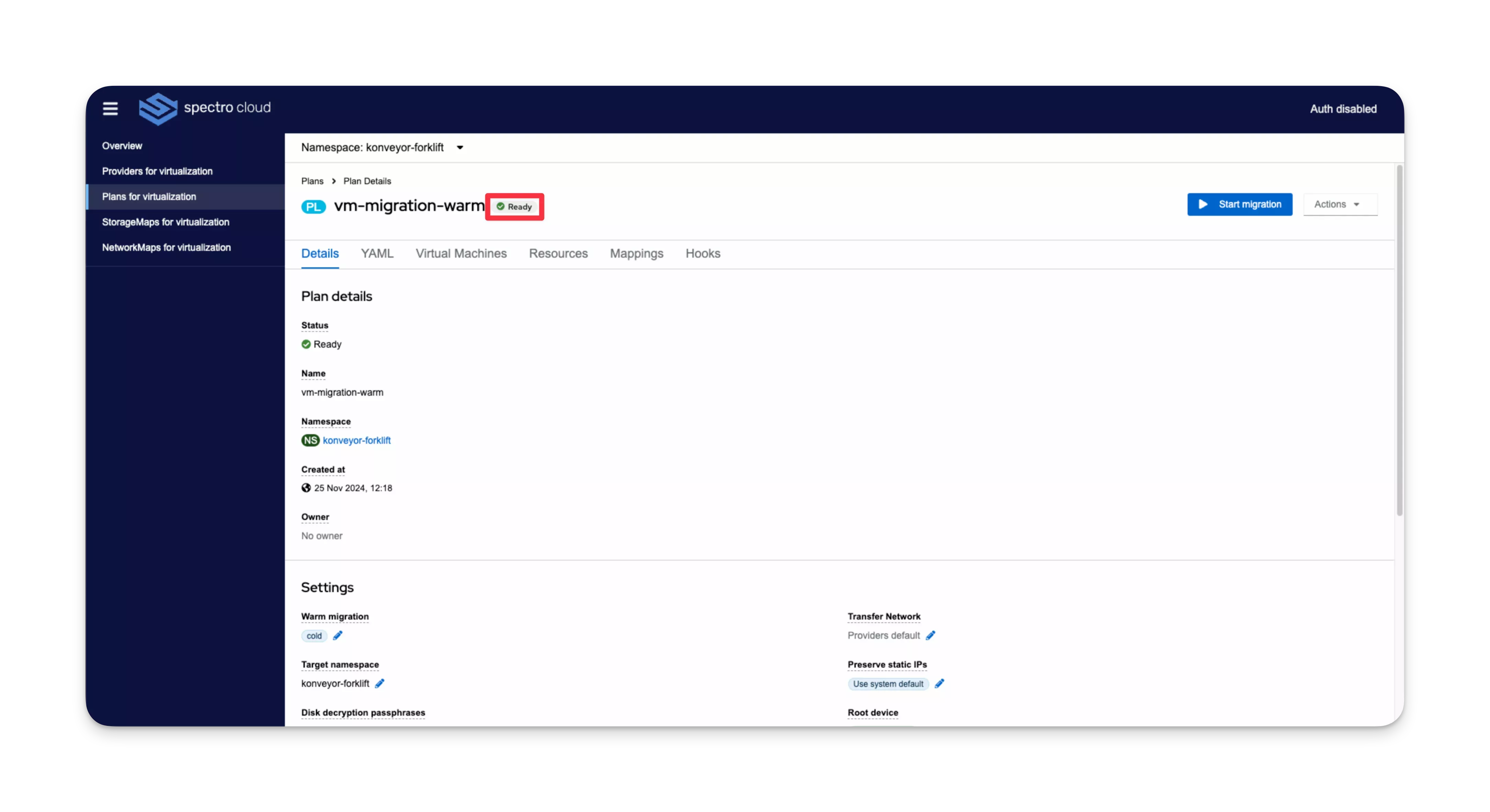
Validate
-
From the left Main Menu, select Plans for virtualization.
-
In the top-left corner, use the Namespace drop-down Menu to select your Kubernetes namespace for the migration.
-
In the table, click on a plan name to view the plan details.
-
In the Details tab, the plan status displays as Ready.
Next Steps
You can now start your migration plans in the VM Migration Assistant. Refer to the Start Migration Plans guide to start migrations.