Architecture
The Palette Virtual Machine Orchestrator (VMO) pack consolidates all components that you need to deploy and manage Virtual Machines (VMs) alongside containers in a Kubernetes host cluster. You can deploy VMO as an add-on cluster profile on top of an existing data center or edge cluster.
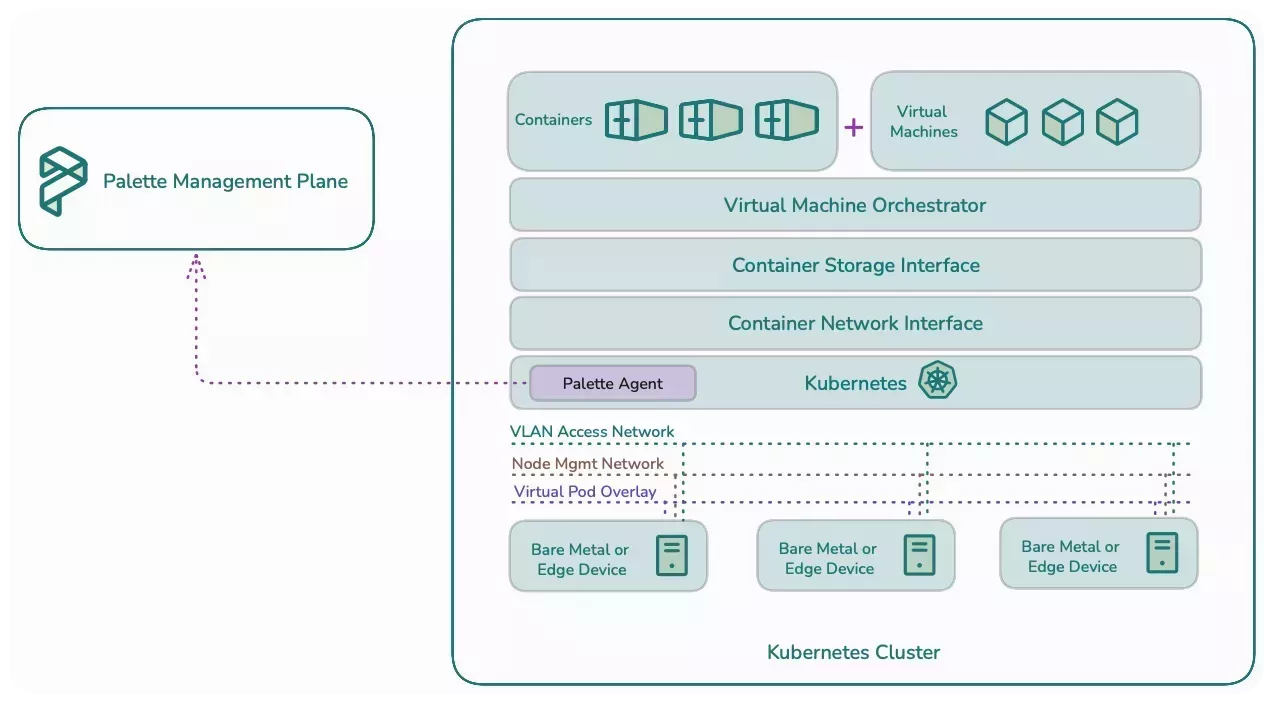
For more detailed information about the technical architecture of VMO, refer to the Spectro Cloud Resource Center. From the left main menu, select the Virtual Machines topic to find the latest version of the Palette VMO Reference Architecture.
Palette VMO Components
By default, Palette VMO includes the following components:
- Descheduler. Enables VM live migration to different nodes in the node pool when the original node is in maintenance mode.
-
Snapshot Controller. Enables you to create VM snapshots. This component is automatically installed when you initiate or schedule cluster backups.
infoPalette installs a snapshot controller into every cluster where backups are scheduled or have been created on-demand in the past. To prevent resource conflicts, ensure that the Volume Snapshot Controller pack is not a layer in your cluster profile before configuring VMO.
-
Spectro VM Dashboard. Enables you to create, manage, and monitor VMs from Palette. The dashboard becomes available once the VMO pack is successfully deployed as part of your cluster profile.
-
KubeVirt. This open source solution enables you to create and manage VMs within Kubernetes clusters. KubeVirt extends Kubernetes with additional virtualization resource types using Kubernetes Custom Resource Definitions (CRD) API.
With KubeVirt, you can use the Kubernetes API to manage VM resources in the same way you would manage standard Kubernetes resources.
tipPalette VMO is pre-configured to use a number of KubeVirt feature gates out of the box, and you can configure additional feature gates as necessary. Refer to the Feature Gates section for more information.
-
KubeVirt CDI. Provides persistent storage for Kubernetes clusters and enables the use of Persistent Volume Claims (PVCs) as disks for KubeVirt VMs.
-
Volume Snapshot Controller. Watches VolumeSnapshot CRD objects and manages the creation and deletion of volume snapshots. A snapshot represents a point-in-time copy of a volume.
-
Multus CNI. Enables multiple network interfaces to attach to Kubernetes pods. In the context of VMO, Multus Controller Network Interface (CNI) automatically creates VLAN interfaces onto which you can place VMs.
Feature Gates
Palette VMO includes the following KubeVirt feature gates by default:
- LiveMigration
- Snapshot
- HotplugVolumes
- VMExport
- ExpandDisks
- HotplugNICs
- VMLiveUpdateFeatures
- CPU Hotplug
For more information on KubeVirt feature gates, refer to the KubeVirt Activating feature gates guide.
MAC Address Management
Palette automatically assigns unique Media Access Control (MAC) addresses to VMs when you create them through the
Palette UI, API, or Terraform. The MAC address always starts with a prefix that
is either 02, 06, 0A, or 0E. The next two octets are generated from a hash of the cluster GUID. It is important
to ensure the remaining three octets are unique for the scope of the VMO cluster. Refer to
this guide
for more information on MAC address assignment in vCenter.
Specify a MAC Address
You can set a VM MAC address by specifying a value in the YAML configuration file under the macAddress field.
If you choose to assign a custom MAC address to a VM, ensure that it is unique and not already in use by any other VM in the cluster. Duplicate MAC addresses can cause network conflicts and connectivity issues.
spec:
template:
spec:
domain:
devices:
interfaces:
- macAddress: "REPLACE_WITH_MAC_ADDRESS"
Next Steps
Now that you understand the architecture behind Palette VMO, you can continue exploring it by reviewing our Environment Setup and Create a VMO Profile pages.