Private Cloud Gateway
When you deploy a Kubernetes cluster in a private data center environment, you must already have a Private Cloud Gateway (PCG) cluster deployed in the data center environment. A PCG enables secure communication between Palette and the private data center environment.
While deploying a PCG, you may encounter one of the following error scenarios. Some scenarios below apply to all data center environments, whereas others apply to a specific data center environment, such as VMware. Each scenario covers a specific problem, including an overview, possible causes, and debugging steps.
Scenario - Clean Up Stuck Namespaces
When force-deleting clusters deployed using a PCG, namespaces on the PCG may get stuck in a
Terminating state when resources within the namespace have
finalizers that cannot complete their
cleanup tasks.
To clean up stuck namespaces on a PCG, we recommend running a script against your PCG or self-hosted management plane cluster on an as-need basis.
Debug Steps
For multi-tenant and dedicated SaaS instances, perform cleanup on any applicable PCGs. For self-hosted Palette and Palette VerteX, clean up any applicable PCGs as well as your management plane cluster if you have used the Palette System Private Gateway to deploy clusters.
- Private Cloud Gateway
- System Private Gateway
-
Log in to Palette or Palette VerteX as a tenant admin.
-
From the left main menu, select Tenant Settings.
-
In the Infrastructure section, select Private Cloud Gateways. Select a PCG with a stuck namespace.
-
From the PCG Overview tab, select Kubeconfig file to download the kubeconfig of your PCG.
-
Open a terminal session on a machine with kubectl installed and set the location of your kubeconfig file as an environment variable. For more information, refer to our Kubectl guide.
export KUBECONFIG=<path-to-PCG-kubeconfig> -
Verify that your PCG contains a namespace stuck in the
Terminatingstate.kubectl get namespace --output custom-columns=NAME:metadata.name,STATUS:status.phase | grep TerminatingExample outputdeleted-cluster-namespace Terminating -
Create the following script.
cat << 'EOF' > cleanup_pcg.sh
#!/bin/bash
#Identify all namespaces stuck in a terminating state
NSTOCLEAN=$(kubectl get ns -o custom-columns=NAME:metadata.name,STATUS:status.phase | grep Terminating | awk '{print $1}')
#Remove finalizers from resources within each stuck namespace
for ns in $NSTOCLEAN
do
echo "Clean up namespace $ns"
RESOURCES="clusters.cluster.x-k8s.io kubeadmcontrolplanes maasclusters vsphereclusters maasmachines vspheremachines vspherevms machines machineset spectroclusters"
#Patch each resource with a finalizer of null, allowing Kubernetes to delete the resources and ultimately the namespace
for r in $RESOURCES
do
kubectl patch $r -n $ns $(kubectl get $r -n $ns -o go-template --template '{{range .items}}{{.metadata.name}}{{" "}}{{end}}') --type merge -p '{"metadata":{"finalizers":null}}'
done
done
EOF -
Set execute permissions and run the script to remove all
Terminatingnamespaces on the PCG.chmod +x cleanup_pcg.sh
./cleanup_pcg.sh -
Run the following command to verify that no
Terminatingnamespaces remain. No output indicates a successful cleanup job.kubectl get namespace --output custom-columns=NAME:metadata.name,STATUS:status.phase | grep Terminating -
Repeat steps 3 - 9 for all PCGs with a namespace stuck in the
Terminatingstate.
-
Log in to your Palette or Palette VerteX system console.
-
From the left main menu, select Enterprise Cluster.
-
From the enterprise cluster Overview tab, select Kubernetes Config File to download the kubeconfig of your management plane cluster.
-
Open a terminal session on a machine with kubectl installed and set the location of your kubeconfig file as an environment variable. For more information, refer to our Kubectl guide.
export KUBECONFIG=<path-to-management-cluster-kubeconfig> -
Verify that your management cluster contains a namespace stuck in the
Terminatingstate.kubectl get namespace --output custom-columns=NAME:metadata.name,STATUS:status.phase | grep TerminatingExample outputdeleted-cluster-namespace Terminating -
Create the following script.
cat << 'EOF' > cleanup_pcg.sh
#!/bin/bash
#Identify all namespaces stuck in a terminating state
NSTOCLEAN=$(kubectl get ns -o custom-columns=NAME:metadata.name,STATUS:status.phase | grep Terminating | awk '{print $1}')
#Remove finalizers from resources within each stuck namespace
for ns in $NSTOCLEAN
do
echo "Clean up namespace $ns"
RESOURCES="clusters.cluster.x-k8s.io kubeadmcontrolplanes maasclusters vsphereclusters maasmachines vspheremachines vspherevms machines machineset spectroclusters"
#Patch each resource with a finalizer of null, allowing Kubernetes to delete the resources and ultimately the namespace
for r in $RESOURCES
do
kubectl patch $r -n $ns $(kubectl get $r -n $ns -o go-template --template '{{range .items}}{{.metadata.name}}{{" "}}{{end}}') --type merge -p '{"metadata":{"finalizers":null}}'
done
done
EOF -
Set execute permissions and run the script to remove all
Terminatingnamespaces on the management cluster.chmod +x cleanup_pcg.sh
./cleanup_pcg.sh -
Run the following command to verify that no
Terminatingnamespaces remain. No output indicates a successful cleanup job.kubectl get namespace --output custom-columns=NAME:metadata.name,STATUS:status.phase | grep Terminating
Scenario - VMware Resources Remain After Cluster Deletion
The Cluster API (CAPI) upgrade in Palette 4.7 introduced new reconciliation behavior for VSphereDeploymentZone and
VSphereFailureDomain resources. Prior to Palette 4.7, when deleting VMware vSphere clusters, these resources were not
deleted with the cluster and remained on the PCG. Beginning with Palette 4.7, these resources
are automatically removed when the cluster is deleted.
After upgrading Palette from 4.6.x to 4.7.x, users may experience slowness or cluster deployment failures when deploying
VMware vSphere clusters if they deployed VMware vSphere clusters using the PCG prior to 4.7. This is due to the upgraded
CAPI controller attempting and failing to reconcile VSphereDeploymentZone and VSphereFailureDomain resources
leftover on the PCG from pre-4.7 cluster deployments.
To continue deploying VMware vSphere clusters using either a standard PCG or Palette's
System Private Gateway, you must manually remove all stale
VSphereDeploymentZone and VSphereFailureDomain resources from your PCG or management plane cluster. This is a
one-time action that must be performed for each PCG and self-hosted instance.
Debug Steps
For multi-tenant and dedicated SaaS instances, remove all stale VSphereDeploymentZone and VSphereFailureDomain
resources from each PCG used to deploy VMware vSphere clusters prior to Palette 4.7. For self-hosted instances, remove
all stale resources from any applicable PCG as well as your management plane cluster if you used the Palette
System Private Gateway to deploy VMware vSphere clusters prior
to Palette 4.7.
- Private Cloud Gateway
- System Private Gateway
-
Log in to Palette or Palette VerteX as a tenant admin.
-
From the left main menu, select Tenant Settings.
-
In the Infrastructure section, select Private Cloud Gateways. Select a PCG used to deploy VMware vSphere clusters prior to version 4.7.
-
From the PCG Overview tab, select Kubeconfig file to download the kubeconfig of your PCG.
-
Open a terminal session on a machine with kubectl installed and set the location of your kubeconfig file as an environment variable. For more information, refer to our Kubectl guide.
export KUBECONFIG=<path-to-PCG-kubeconfig> -
Run the following command to view a list of all
VSphereDeploymentZoneandVSphereFailureDomainresources on your PCG.kubectl get VSphereDeploymentZone,VSphereFailureDomainExample outputNAME AGE
vspheredeploymentzone.infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/doc-1667-cluster2 150d
vspheredeploymentzone.infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/doc-1667-cluster2-cp 150d
vspheredeploymentzone.infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/doc-pcg-cluster3-cp 170d
NAME AGE
vspherefailuredomain.infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/doc-1667-cluster2 150d
vspherefailuredomain.infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/doc-1667-cluster2-cp 150d
vspherefailuredomain.infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/doc-pcg-cluster3-cp 170d -
Delete all stale
VSphereDeploymentZoneandVSphereFailureDomainobjects.dangerDo not delete any objects associated with the PCG or clusters with an
Activestatus.kubectl delete VSphereDeploymentZone <object-name>
kubectl delete VSphereFailureDomain <object-name>Example commandkubectl delete VSphereDeploymentZone doc-1667-cluster2 doc-1667-cluster2-cp
kubectl delete VSphereFailureDomain doc-1667-cluster2 doc-1667-cluster2-cp -
Confirm the stale resources have been deleted. In the following example, only the PCG resources remain.
kubectl get VSphereDeploymentZone,VSphereFailureDomainExample outputNAME AGE
vspheredeploymentzone.infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/doc-pcg-cluster3-cp 170d
NAME AGE
vspherefailuredomain.infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/doc-pcg-cluster3-cp 170d -
Repeat steps 3 - 8 for each PCG used to deploy VMware vSphere clusters prior to Palette 4.7.
-
Log in to your Palette or Palette VerteX system console.
-
From the left main menu, select Enterprise Cluster.
-
From the enterprise cluster Overview tab, select Kubernetes Config File to download the kubeconfig of your management plane cluster.
-
Open a terminal session on a machine with kubectl installed and set the location of your kubeconfig file as an environment variable. For more information, refer to our Kubectl guide.
export KUBECONFIG=<path-to-management-cluster-kubeconfig> -
Run the following command to view a list of all
VSphereDeploymentZoneandVSphereFailureDomainobjects on your management cluster.kubectl get VSphereDeploymentZone,VSphereFailureDomainExample outputNAME AGE
vspheredeploymentzone.infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/doc-1667-cluster2 150d
vspheredeploymentzone.infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/doc-1667-cluster2-cp 150d
vspheredeploymentzone.infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/doc-pcg-cluster3-cp 170d
NAME AGE
vspherefailuredomain.infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/doc-1667-cluster2 150d
vspherefailuredomain.infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/doc-1667-cluster2-cp 150d
vspherefailuredomain.infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/doc-pcg-cluster3-cp 170d -
Delete all stale
VSphereDeploymentZoneandVSphereFailureDomainobjects.dangerDo not delete any objects associated with the PCG or clusters with an
Activestatus.kubectl delete VSphereDeploymentZone <object-name>
kubectl delete VSphereFailureDomain <object-name>Example commandkubectl delete VSphereDeploymentZone doc-1667-cluster2 doc-1667-cluster2-cp
kubectl delete VSphereFailureDomain doc-1667-cluster2 doc-1667-cluster2-cp -
Confirm the stale resources have been deleted. In the following example, only the PCG resources remain.
kubectl get VSphereDeploymentZone,VSphereFailureDomainExample outputNAME AGE
vspheredeploymentzone.infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/doc-pcg-cluster3-cp 170d
NAME AGE
vspherefailuredomain.infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/doc-pcg-cluster3-cp 170d
Scenario - PCG Installer VM IP Address Assignment Error
When deploying a PCG in VMware vSphere, the VMs that make up the cluster nodes may fail to get an IP address.
If the PCG node fails to get an IP address assigned, it implies a networking error or an incomplete cloud-init. The selected IP allocation scheme specified in the network settings of the PCG installation assigns an IP address to the PCG node. The IP allocation scheme offers two options - static IP or DHCP. You must check the selected IP allocation scheme for troubleshooting.
Debug Steps
-
If you chose the static IP allocation scheme, ensure you have correctly provided the values for the gateway IP address, DNS addresses, and static IP subnet prefix. Check that the subnet prefix you provided allows the creation of an IP pool with sufficient IP addresses to allocate to the new PCG installer VM.
-
If you chose the DHCP allocation scheme, check that the DHCP service is available on the DHCP server. Restart the service if it's not in an active state.
-
If the DHCP server is active, recheck the DHCP scope and the DHCP reservations. The DHCP scope defines the range of IP addresses that the DHCP server allocates on the selected network. You must have sufficient IP addresses from the DHCP scope for dynamic allocation.
-
If you chose the DHCP allocation scheme, ensure Dynamic DNS is enabled in the DHCP server. A Dynamic DNS is only required if you are using DHCP. Dynamic DNS is not required for a static IP allocation scheme.
-
If there are no network-related issues, SSH into the PCG installer VM using the username
ubuntuand the SSH public key you provided during the installation. -
Inspect the log files in the /var/log directory.
-
Examine the cloud-init logs for potential errors or warnings related to the IP address assignment.
-
If the problem persists, email the log files to our support team at support@spectrocloud.com.
Scenario - PCG Cluster Provisioning Stalled or Failed
After you finish configuring the cloud gateway in Palette, the PCG cluster provisioning process may take up to 15 minutes to finish the PCG cluster deployment.
However, if the PCG cluster provisioning gets stuck, it could hint at incorrect cloud gateway configurations,
unavailable IP addresses for the worker nodes, or the inability to perform a Network Time Protocol (NTP) sync.
Debug Steps
-
Log in to Palette.
-
Navigate to the left Main Menu and select Tenant Settings. From the Tenant settings menu, select Private Cloud Gateways.
-
Click on the newly provisioned PCG cluster to review its details.
-
Click on the Events tab.
-
Examine all events in the Events tab to identify specific errors or issues. Each event will have a status, timestamp, associated service name, and orchestration details.
-
If you encounter one of the following error events -
Failed to deploy image: Failed to create govomiClientorNo route to host, refer to the remediation steps in the Scenario - No Route to the Kubernetes API Server section, respectively. -
If you encounter errors other than the ones mentioned in the previous step, it is possible that the cluster configuration or the DNS settings are not set correctly. You can review and edit the cluster configuration in the cluster settings. The screenshot below highlights the cluster configuration section in the cluster settings blade.
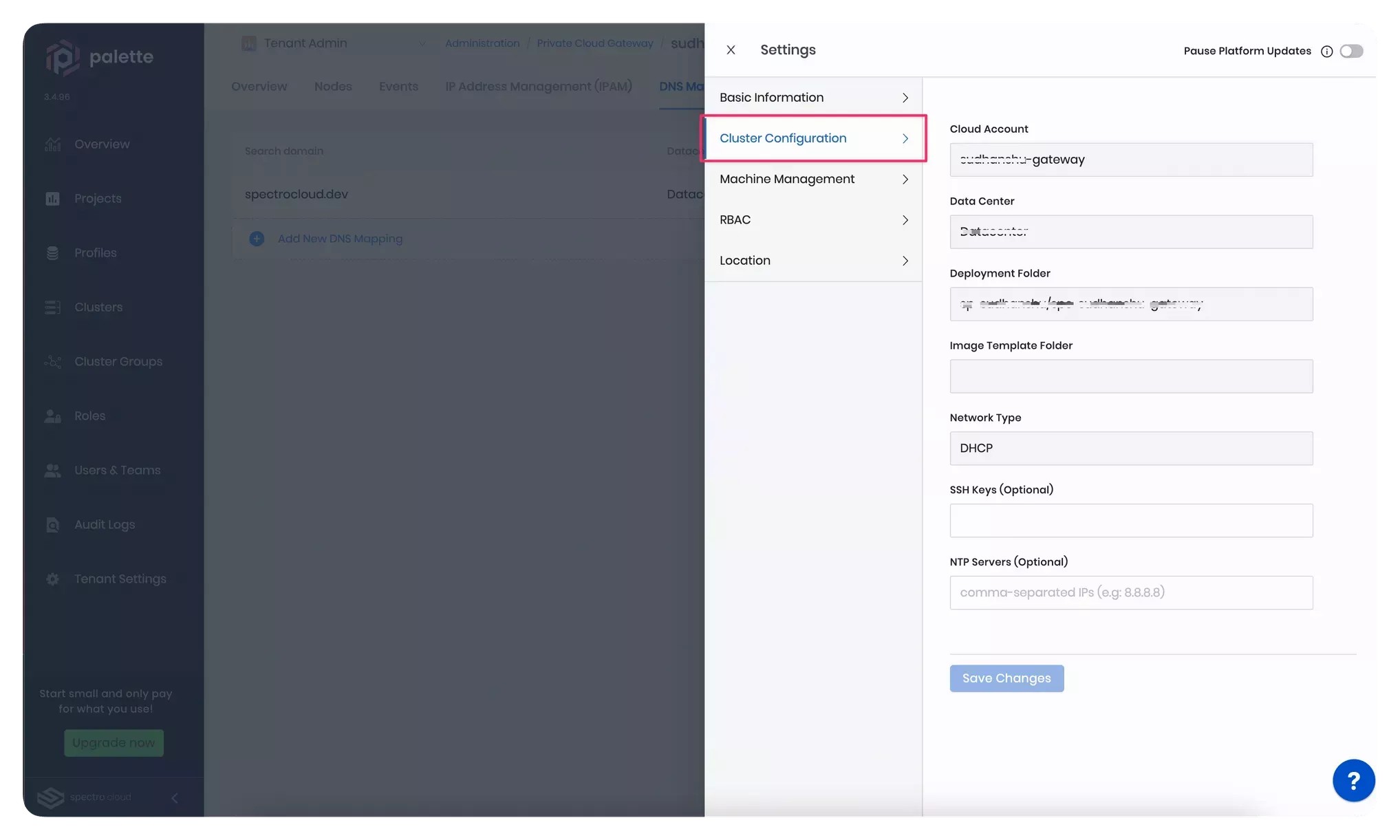
-
If the cluster settings look correct, ensure the search domain is correctly defined in the fault domain's DNS settings. The screenshot below highlights how you can review and edit the DNS mapping of an existing PCG cluster.
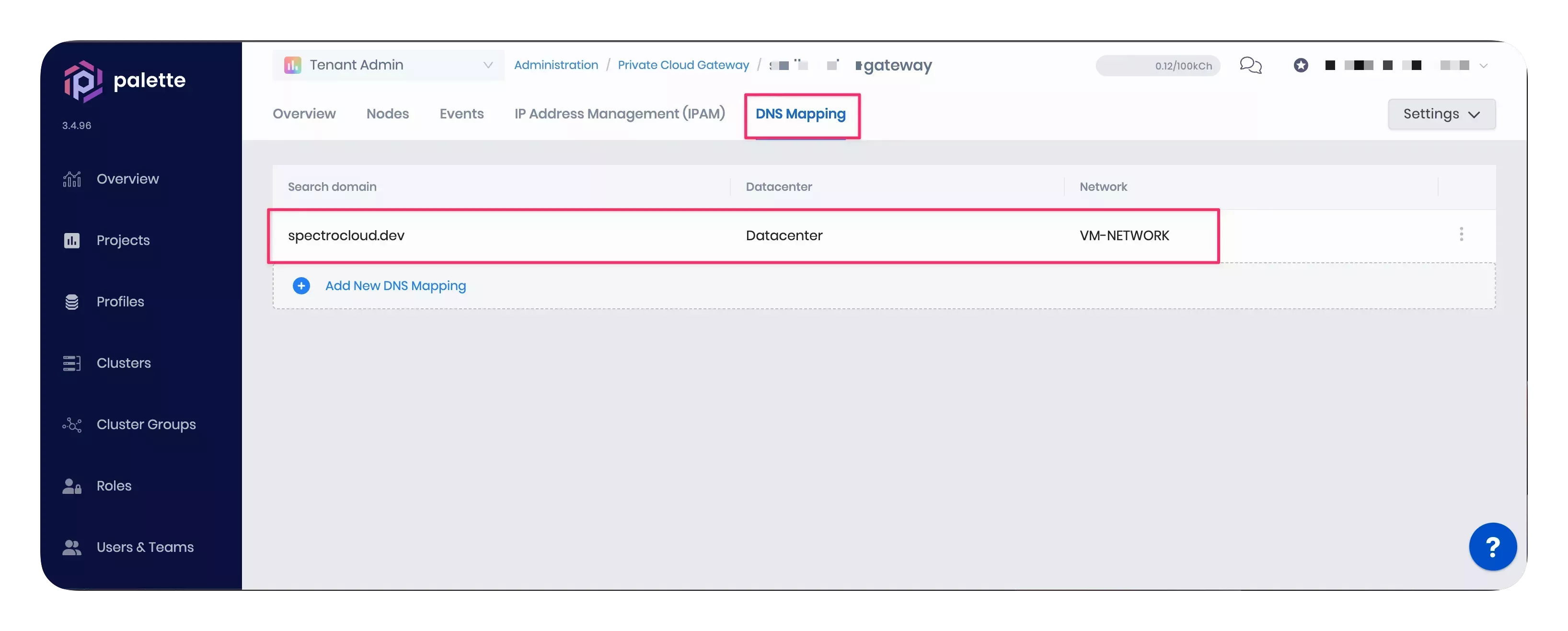
-
If the problem persists, download the cluster logs from Palette. The screenshot below will help you locate the button to download logs from the cluster details page.
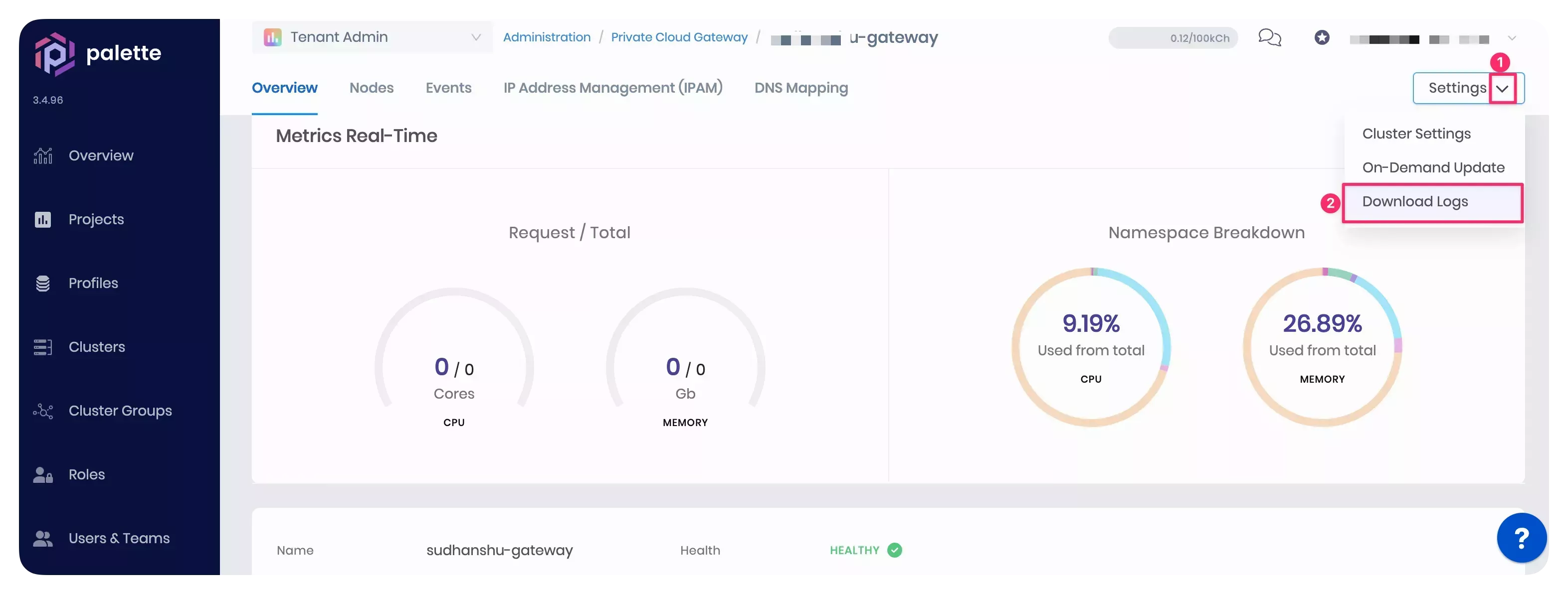
-
Share the logs with our support team at support@spectrocloud.com.
Scenario - No Route to the Kubernetes API Server
If one of the event logs displays the No route to host. error. The error indicates an issue with the PCG cluster nodes
attempting to connect to the cluster's Kubernetes API server. This issue can occur due to improper networking
configuration or an error in the cloud-init process.
Debug Steps
-
Check the data center network settings. Ensure no network restrictions, firewalls, or security groups block communication between the nodes and the API server.
-
If you use the DHCP allocation scheme, check that the DHCP service is available on the DHCP server. Restart the service if it's not in an active state.
-
If you use the DHCP allocation scheme, ensure Dynamic DNS is enabled in the DHCP server. A Dynamic DNS is only required if you are using DHCP. Dynamic DNS is not required for a static IP allocation scheme.
-
Check the Kubernetes API server status. The Kubernetes API server must be active and healthy on the control plane node. Use the following steps to check the status.
-
Switch to Palette.
-
Navigate to the Tenant Settings > Private Cloud Gateways page.
-
Click on the newly provisioned PCG cluster to review its details.
-
Download the PCG cluster's kubeconfig file from the Overview tab. Click on the kubeconfig file name to download it to your local machine, as highlighted in the screenshot below.
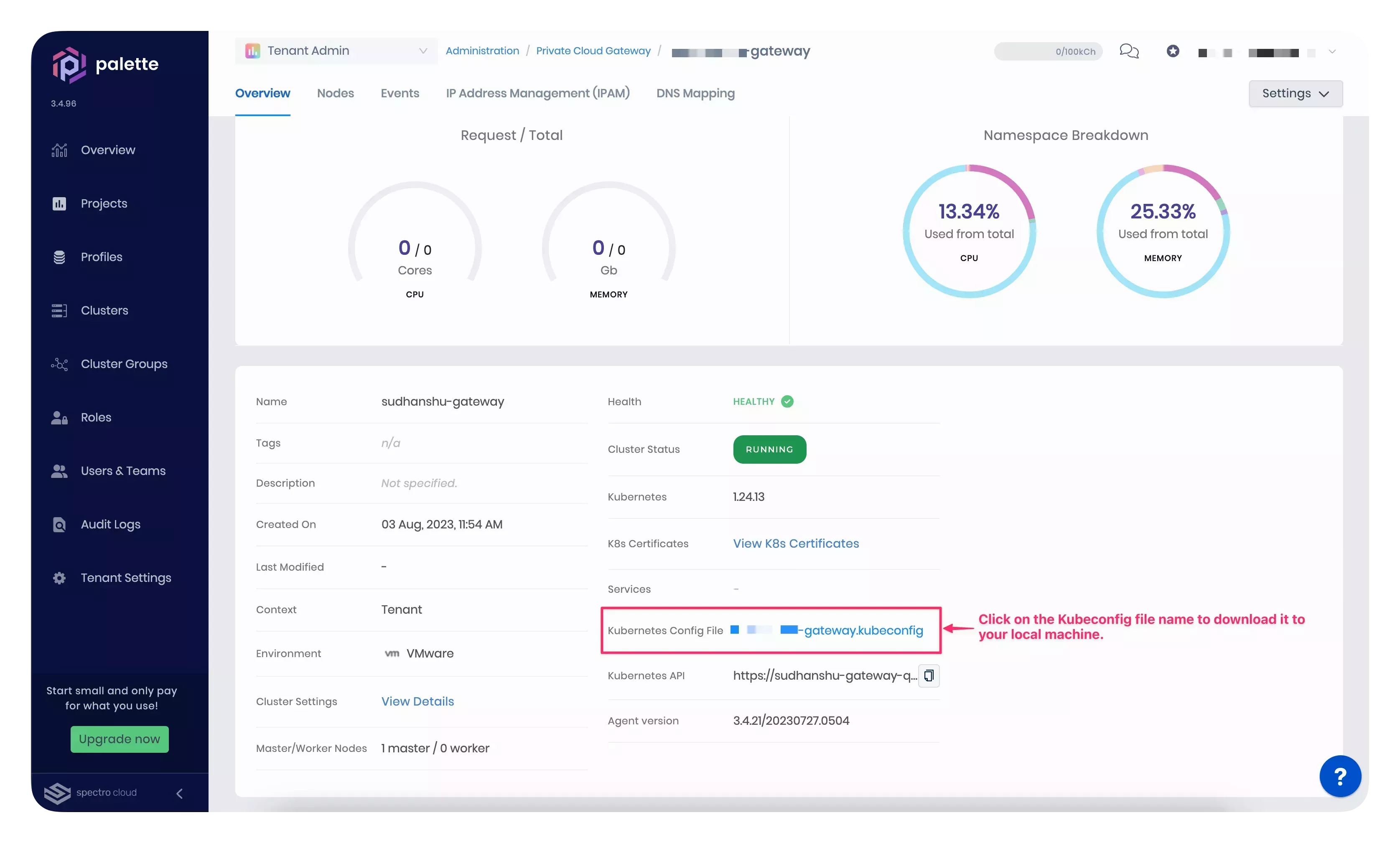
-
After you download the PCG cluster's kubeconfig file, use the following commands to make a GET request to one of the Kubernetes API server endpoints,
/readyzor'/livez'. Replace[path_to_kubeconfig]placeholder with the path to the kubeconfig file you downloaded in the previous step. A status codeokor200indicates the Kubernetes API server is healthy.kubectl --kubeconfig [path_to_kubeconfig] get --raw='/readyz' -
If the previous command does not return an
ok, use the command below to make a verbose GET request by specifying theverboseparameter. The output will display the individual health checks so you can decide on further debugging steps based on the failed checks.kubectl --kubeconfig [path_to_kubeconfig] get --raw='/readyz?verbose'
-
-
If the PCG node has an IP address assigned, SSH into the VM using the username
spectroand the public SSH key you provided during the PCG install. If you installed the PCG onto an existing Kubernetes cluster, contact your Kubernetes system administrator for the SSH credentials. -
Navigate to the /var/log directory containing the log files.
-
Examine the cloud-init and system logs for potential errors or warnings.
-
If the problem persists, reach out to our support team at support@spectrocloud.com.
Scenario - Permission Denied to Provision
if you receive the event log message "Permission to perform this operation denied" error.
You must have the necessary permissions to provision a PCG cluster in the VMware environment. If you do not have adequate permissions, the PCG cluster provisioning will fail, and you will get the above-mentioned error in the events log.
Debug Steps
-
Ensure you have all the permissions listed in the VMware Privileges section before proceeding to provision a PCG cluster.
-
Contact your VMware administrator if you are missing any of the required permissions.
-
Delete the existing PCG cluster and redeploy a new one so that the new permissions take effect.
Scenario - vSphere Controller Pod Fails to Start in Single Node PCG Cluster
In a single-node PCG cluster, the vSphere controller pod may fail to start due to no matching node affinity rules. If you encounter this issue, follow the steps below to resolve it.
Debug Steps
-
Connect to the PCG cluster using the
kubectlcommand-line tool. You can find the kubeconfig file in the PCG cluster's details page in Palette. Log in to Palette and navigate to the left Main Menu and select Tenant Settings. From the Tenant settings Menu, select Private Cloud Gateways. Select the PCG cluster that is deployed in the VMware vSphere environment to access the details page. For additional guidance on how to setup kubectl, check out the Access Cluster with CLI page. -
Issue the following command to get the vSphere controller pod's status. Take note of the pod's name.
kubectl get pods --namespace kube-system -
If the vSphere controller pod is in a
Pendingstate, issue the following command to delete the existing pod and force a restart.kubectl delete pod <vSphere-controller-pod-name> --namespace kube-system -
After deleting the pod, issue the following command to check the pod's status.
kubectl get pods --namespace kube-system -
If the pod is still in a
Pendingstate, check the pod's events to investigate the issue.kubectl describe pod <vSphere-controller-pod-name> --namespace kube-system -
If the problem persists, reach out to our support team at support@spectrocloud.com.