MicroK8s
Support Lifecycle
We support different Kubernetes distributions, such as MicroK8s, K3s, and RKE2, until their official End-of-Life (EOL). The EOL is set by the respective owner. Once we stop supporting the minor version, we initiate the deprecation process. Refer to the Kubernetes Support Lifecycle guide to learn more.
Versions Supported
- 1.28.x
- 1.27.x
- 1.26.x
Usage
To use MicroK8s, select it as the Kubernetes distribution when choosing the Kubernetes layer during the cluster profile creation. Remember that the cloud type must be either AWS or MAAS, and the OS layer must be Ubuntu 22.04.
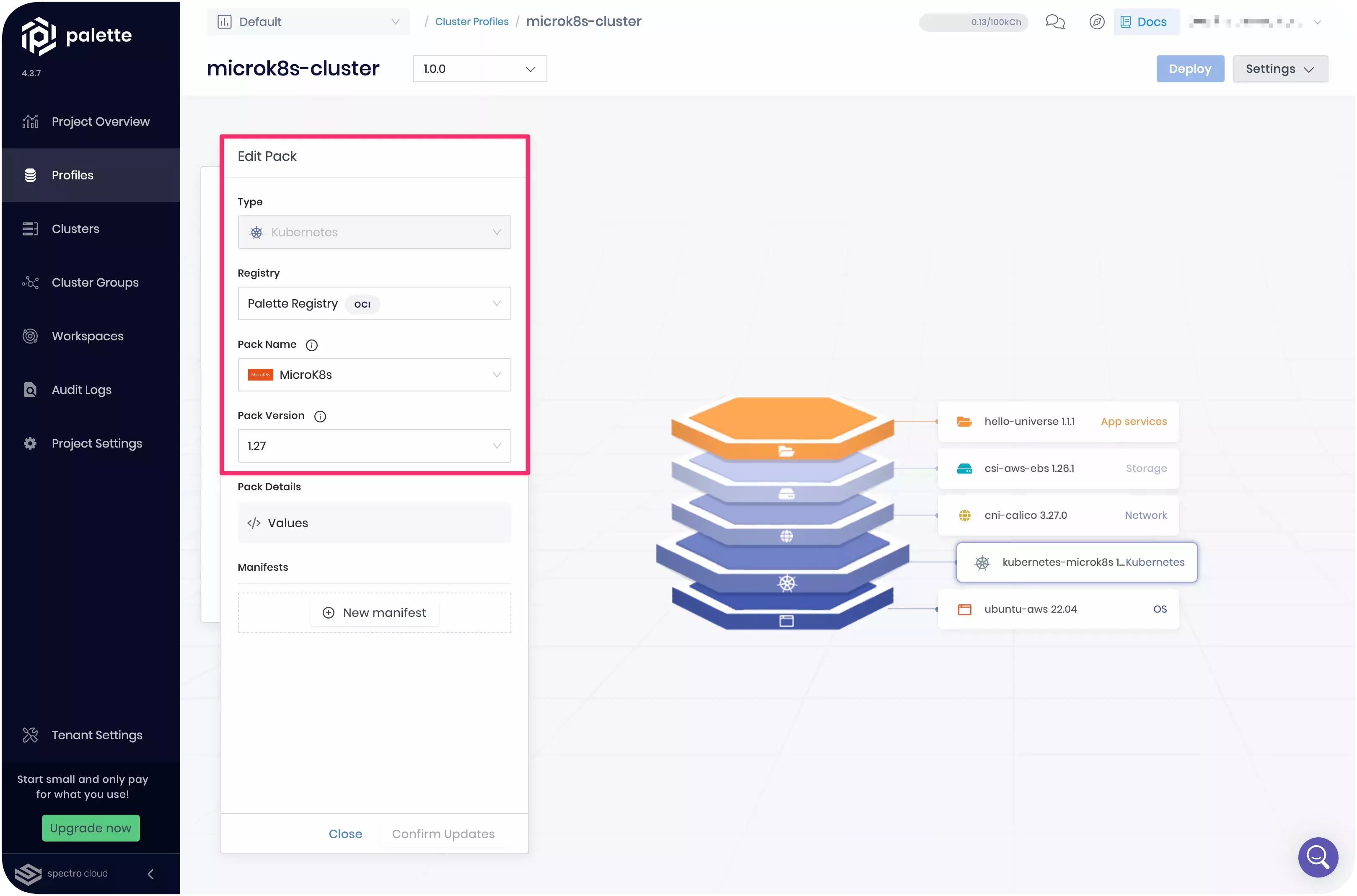
MicroK8s clusters use the Calico CNI by default. However, this default installation was disabled due to Palette's requirement for a CNI layer to be present in the cluster profiles. This way, users can choose their preferred CNI layer during the cluster profile creation.
Upgrade Strategy
The upgrade strategy describes how to replace existing control plane nodes with new ones during upgrades.
You can specify the upgrade strategy during cluster profile creation by editing the value of the upgradeStrategy
parameter in the MicroK8s pack YAML file displayed under the Pack Details section.
Before upgrading your cluster, review the Known Issues and the Kubernetes Upgrades pages to learn about the limitations associated with MicroK8s upgrades.
The MicroK8s pack supports three types of upgrade strategies:
-
InPlaceUpgrade- Performs an in-place upgrade of the control plane. For clusters with one control plane and one worker node,InPlaceUpgradetemporarily shuts down the API server. This is the default upgrade strategy. -
RollingUpgrade- This upgrade strategy deletes the current control plane node before creating a new one. -
SmartUpgrade- Performs an in-place upgrade of the control plane on clusters with fewer than three control plane nodes, and a rolling upgrade on clusters with three or more control plane nodes.
Using MicroK8s with the AWS EBS Pack
When using the AWS EBS pack with MicroK8s,
you need to change the EBS CSI pack node.kubelet parameter from /var/lib/kubelet to
/var/snap/microk8s/common/var/lib/kubelet.
node:
env: []
kubeletPath: /var/lib/kubelet
node:
env: []
kubeletPath: /var/snap/microk8s/common/var/lib/kubelet
Troubleshoot
Scenario - Backup and Restore Fails with Restic
If you encounter errors backing up or restoring a MicroK8s cluster with restic, it may be related to the Velero issue 4035. You can resolve this issue by using the following workaround.
-
Issue the command below to get the
resticdaemonset pod and its namespace.kubectl get pods --selector name=restic --all-namespacesNAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
cluster-66f0f593841168d5eec8962e restic-4lj7p 0/1 Terminating 3 2m -
Issue the following command to patch the
resticdaemonset pod. Replacecluster-xxxxxxxxxwith the namespace of yourresticdaemonset pod.kubectl ---namespace cluster-xxxxxxxxx patch daemonset restic --patch '{"spec":{"template":{"spec":{"volumes":[{"name":"host-pods","hostPath":{"path":"/var/snap/microk8s/common/var/lib/kubelet/pods"}}]}}}}' -
Verify that the
resticdaemonset pod is patched. Replacecluster-xxxxxxxxxwith the namespace of yourresticdaemonset pod.kubectl --namespace cluster-xxxxxxxxx get daemonset restic -o jsonpath='{.spec.template.spec.volumes}'[
{
"name": "cloud-credentials",
"secret": {
"defaultMode": 420,
"secretName": "velero"
}
},
{
"hostPath": {
"path": "/var/snap/microk8s/common/var/lib/kubelet/pods",
"type": ""
},
"name": "host-pods"
}
] -
Backup and restore operations will now work as expected.
Container Network Interface (CNI)
MicroK8s clusters use the Calico CNI by default. However, this default installation was disabled due to Palette's requirement for a CNI layer to be present in the cluster profiles. This way, users can choose their preferred CNI layer during the cluster profile creation.
Upgrade Strategy
The upgrade strategy describes how to replace existing control plane nodes with new ones during upgrades.
You can specify the upgrade strategy during cluster profile creation by editing the value of the upgradeStrategy
parameter in the MicroK8s pack YAML file displayed under the Pack Details section.
Before upgrading your cluster, review the Known Issues and the Kubernetes Upgrades pages to learn about the limitations associated with MicroK8s upgrades.
The MicroK8s pack supports three types of upgrade strategies:
-
InPlaceUpgrade- Performs an in-place upgrade of the control plane. For clusters with one control plane and one worker node,InPlaceUpgradetemporarily shuts down the API server. -
RollingUpgrade- The default upgrade strategy that deletes the current control plane node before creating a new one. -
SmartUpgrade- Performs an in-place upgrade of the control plane on clusters with fewer than three control plane nodes, and a rolling upgrade on clusters with three or more control plane nodes.
Troubleshoot
Scenario - Backup and Restore Fails with Restic
If you encounter errors backing up or restoring a MicroK8s cluster with restic, it may be related to the Velero issue 4035. You can resolve this issue by using the following workaround.
-
Issue the command below to get the
resticdaemonset pod and its namespace.kubectl get pods --selector name=restic --all-namespacesNAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
cluster-66f0f593841168d5eec8962e restic-4lj7p 0/1 Terminating 3 2m -
Issue the following command to patch the
resticdaemonset pod. Replacecluster-xxxxxxxxxwith the namespace of yourresticdaemonset pod.kubectl ---namespace cluster-xxxxxxxxx patch daemonset restic --patch '{"spec":{"template":{"spec":{"volumes":[{"name":"host-pods","hostPath":{"path":"/var/snap/microk8s/common/var/lib/kubelet/pods"}}]}}}}' -
Verify that the
resticdaemonset pod is patched. Replacecluster-xxxxxxxxxwith the namespace of yourresticdaemonset pod.kubectl --namespace cluster-xxxxxxxxx get daemonset restic -o jsonpath='{.spec.template.spec.volumes}'[
{
"name": "cloud-credentials",
"secret": {
"defaultMode": 420,
"secretName": "velero"
}
},
{
"hostPath": {
"path": "/var/snap/microk8s/common/var/lib/kubelet/pods",
"type": ""
},
"name": "host-pods"
}
] -
Backup and restore operations will now work as expected.
Container Network Interface (CNI)
MicroK8s clusters use the Calico CNI by default. However, this default installation was disabled due to Palette's requirement for a CNI layer to be present in the cluster profiles. This way, users can choose their preferred CNI layer during the cluster profile creation.
Upgrade Strategy
The upgrade strategy describes how to replace existing control plane nodes with new ones during upgrades.
You can specify the upgrade strategy during cluster profile creation by editing the value of the upgradeStrategy
parameter in the MicroK8s pack YAML file displayed under the Pack Details section.
Before upgrading your cluster, review the Known Issues and the Kubernetes Upgrades pages to learn about the limitations associated with MicroK8s upgrades.
The MicroK8s pack supports three types of upgrade strategies:
-
InPlaceUpgrade- Performs an in-place upgrade of the control plane. For clusters with one control plane and one worker node,InPlaceUpgradetemporarily shuts down the API server. -
RollingUpgrade- The default upgrade strategy that deletes the current control plane node before creating a new one. -
SmartUpgrade- Performs an in-place upgrade of the control plane on clusters with fewer than three control plane nodes, and a rolling upgrade on clusters with three or more control plane nodes.
Terraform
You can reference the MicroK8s pack in Terraform with the following data resource.
data "spectrocloud_registry" "public_registry" {
name = "Public Repo"
}
data "spectrocloud_pack" "k8s" {
name = "kubernetes-microk8s"
version = "1.27"
registry_uid = data.spectrocloud_registry.public_registry.id
}