Order of Operations
Palette provisions standard upstream Kubernetes clusters using Cluster API. Cluster API is a Kubernetes sub-project focused on providing declarative APIs and tooling to simplify provisioning, upgrading, and operating multiple Kubernetes clusters.
Check out the Cluster API concepts page for a detailed explanation of the components and concepts used in the Cluster API. Cluster API is a Kubernetes sub-project and different from the Kubernetes API that you use to interact with your Kubernetes clusters.
Cluster API automates cluster lifecycle management for platform operations. It ensures a consistent experience in cluster deployment across different infrastructure environments.
Cluster API Provider Versions
Palette leverages the following Cluster API providers internally. Each provider enables the provisioning, management, and operation of Kubernetes clusters across various cloud platforms through the Kubernetes Cluster API project.
Workload Cluster Provisioning
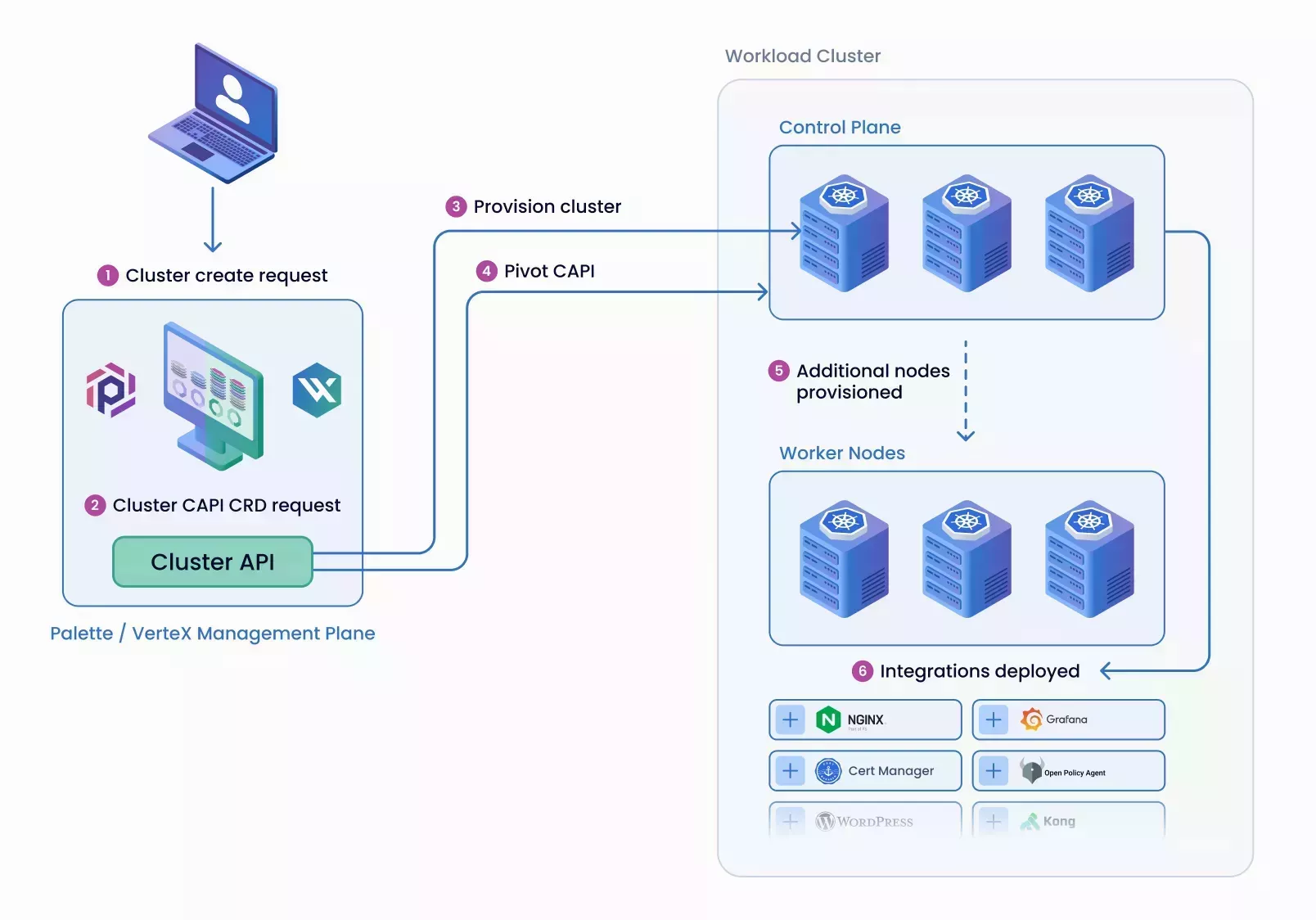
The following diagram illustrates the order of operations that make up the workload cluster provisioning process.
-
A user submits a request to Palette for a new Kubernetes cluster. The request may come from the UI, API, or Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools such as Terraform or Crossplane.
-
Palette creates Cluster-API (CAPI) custom-resource specifications for the target cloud, such as AWS, GCP, etc. For example, in VMware, this would translate to the following resources getting created: Cluster, vSphereCluster, KubeadmControlPlane, and VSphereMachineTemplate. These resources are created in the Palette internal management plane.
-
Cluster API and the respective cluster-api provider, specific to the target platform, such as cluster-api-provider-vsphere, provisions the first control-plane node (CP-A) on the target cloud.
-
When CP-A is operational, the Palette management platform will install a Palette agent into the workload cluster and then perform a pivot of Cluster API resources. This means that Cluster API resources and their responsibilities are now handled by the workload cluster, not the Palette management plane.
-
CP-A agent will retrieve the required specifications for the cluster, such as the number of nodes. CP-A will generate and update the remaining CAPI resources, e.g: update replicas to 3 for KubeadmControlPlane and create the worker's MachineDeployment or VSphereMachineTemplate. The Cluster API active in CP-A will provision the remaining control plane and worker nodes.
-
The Palette agent will install all the additional add-ons as the cluster profile specifies.
We do not hard code credentials. Palette uses the cloud-init process to inject the user-defined SSH keys into the clusters.
Why Palette Pivots?
Palette's decentralized model is based on a "decentralized management" design with local policy enforcement that allows for a scalable architecture.
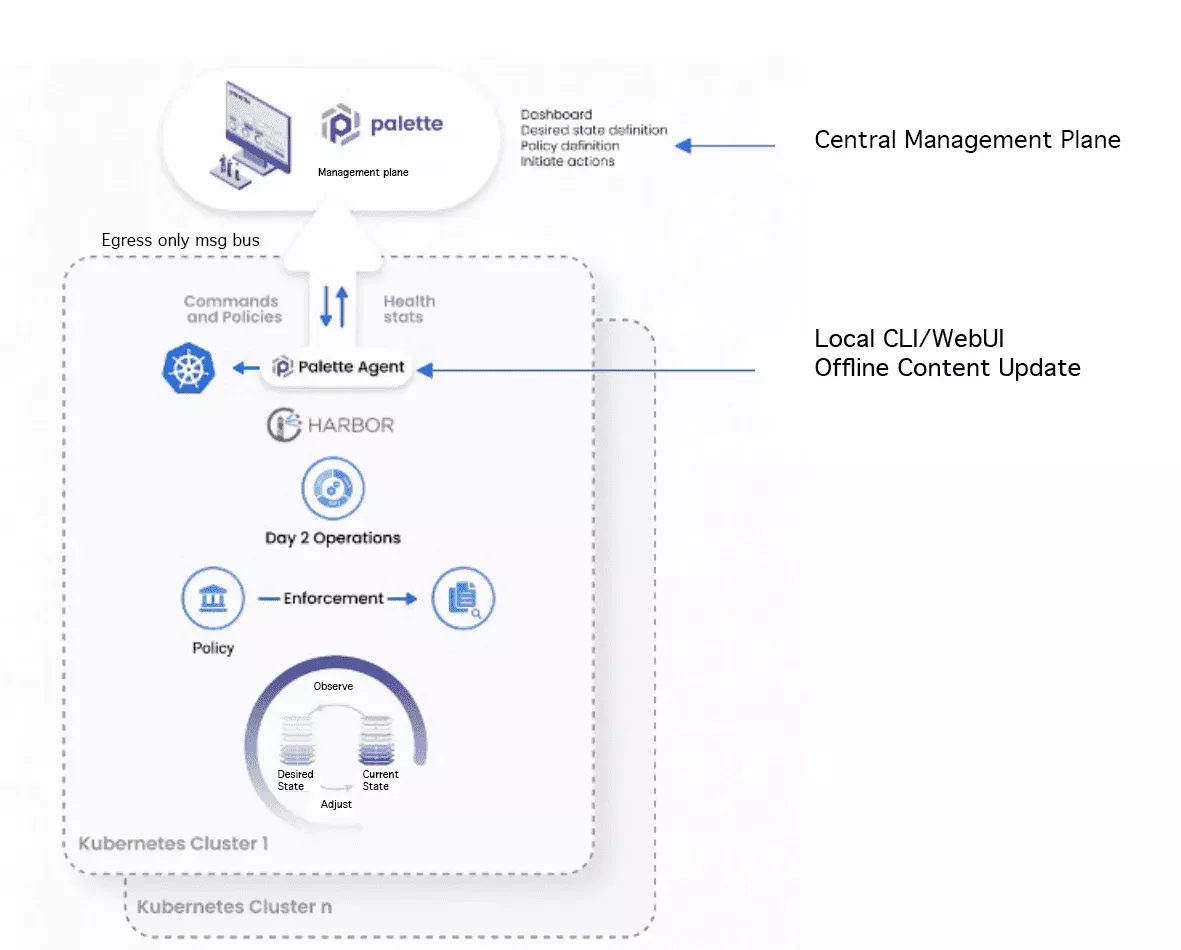
As part of the workload for the Kubernetes cluster provisioning, only the first control-plane node is launched by the Cluster API active in the Palette management cluster. Once the control plane node is operational, Cluster API resources are pivoted from the Palette management platform into the target workload cluster.
The target workload cluster is responsible for provisioning and maintaining the remaining control plane and worker nodes. All Day-2 operations, which may result in node changes, including the operating system and Kubernetes upgrades, node scaling, and Kubernetes SSL certificate rotation, are triggered by changes to Cluster API resources in the target workload cluster.
Palette pivots Cluster API resources from the Palette management platform to the workload clusters for reasons such as:
-
Scalability - The central management platform, Palette, can scale to meet the demand of all your workload clusters as the number of workload clusters and nodes increase in size. The workload cluster manages its own lifecycle and resources through guidance from the Palette management platform.
-
Resiliency - If the management platform were to experience an outage, the workload clusters would retain their capabilities, such as auto-recovery, launching of new nodes on failures, auto-scaling, and other features.
-
Network resiliency - The decentralized design supports use cases where the workload clusters can still operate in intermittent and disconnected network availability situations.